Saturday 27 May 2017
Tuesday 23 May 2017
Internet cemsorship in public library
I wanted to look at the censorship and internet infiltration and how does it affect the people and what is the role of public library. By looking at the definition of Internet censorship there is a element of control, suppression of people's right by certain authorities by putting restriction on what information is accessible to public. And you cannot also note that there is high censorship in countries oppressed people and those countries all form of control
Internet censorship is the control or suppression of what can be accessed, published, or viewed on the Internet enacted by regulators, or on their own initiative. ... Other areas of censorship include copyrights, defamation, harassment, and obscene material. Support for and opposition to Internet censorship also varies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LDtSsYGKAp8
Jan 31, 2017 - Uploaded by The Audiopedia
Internet censorship puts restrictions on what information can be publicized or viewed on the Internet. Governments and other organizations commonly use internet censorship to block access to copyrighted information as well as to harmful or sensitive content. However, internet censorship canalso be used as a propaganda method to promote specific religions and political agendas. https://www.iplocation.net/internet-censorship
censorship: What you need to know - BBC News
www.bbc.com/news/.../internet-censorship-what-you-need-to-know
What is censorship for kids?
cen·sor·ship. Use censorship in a sentence. noun. The definition of censorship is the practice of limiting access to information, ideas or books in order to prevent knowledge or freedom of thought. Banning controversial books is an example of censorship.www.yourdictionary.com/censorship
Censorship is the act or practice of suppressing the speech or public communication which is considered objectionable, harmful and sensitive, by a government, media outlet or other controlling bodies. This public content is censored for many reasons that the active bodies believe are immoral.Dec 7, 2012
Reasons for censorship
There is lot of risks for children why need censorship
Censorship on stories
Internet censorship in South Africa
South Africa is not individually classified by the OpenNet Initiative, but is included in ONI's regional overview for sub-Saharan Africa.[1]
Digital media freedom is generally respected in South Africa. Political content is not censored, and neither bloggers nor content creators are targeted for their online activities. In 2013 Freedom House rated South Africa's "Internet Freedom Status" as "Free".[2]
In 2006, the government of South Africa began prohibiting sites hosted in the country from displaying X18 (explicitly sexual) and XXX content (including child pornography and depictions of violent sexual acts); site owners who refuse to comply are punishable under the Film and Publications Act 1996. In 2007 a South African "sex blogger" was arrested
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_censorship_in_South_Africa
Digital media freedom is generally respected in South Africa. Political content is not censored, and neither bloggers nor content creators are targeted for their online activities. In 2013 Freedom House rated South Africa's "Internet Freedom Status" as "Free".[2]
In 2006, the government of South Africa began prohibiting sites hosted in the country from displaying X18 (explicitly sexual) and XXX content (including child pornography and depictions of violent sexual acts); site owners who refuse to comply are punishable under the Film and Publications Act 1996. In 2007 a South African "sex blogger" was arrested
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_censorship_in_South_Africa
Laws and regulations. Online media in South Africa is currently regulated under the Films and Publications Act of 1996 as amended. ... Their document proposes to make it illegal for Internet service providers in South Africa to distribute or permit the distribution of pornography
The Film and Publication Board has published the final version of its Online Regulation Policy on its website.
It is to be submitted to the Minister of Communications for approval and publication in the Government Gazette, after which it will have legal force, said Ellipsis Regulatory Solutions.
Ellipsis said the policy is structured into four sections: online distribution of “television films” and games, user-generated content (UGC), complaints, and self-classification.
Ellipsis regulatory expert Dominic Cull said this redraft of the original policy document, while problematic in some respects, is a significant improvement over the previous version.
The new policy was revised with the help of Norton Rose Attorneys, and the FPB said it considered all inputs received to develop the new document.
Among the improvements was the FPB’s approach to user-generated content.
https://mybroadband.co.za/news/internet/164354-south-africas-new-internet-censorship-law-fpb-will-force-isps-to-block-online-content.html
To conclude, internet censorship exists to
- prevent individuals accessing copyrighted information.
- stop people from viewing harmful or sensitive content.
- promote particular religions and political ideas.
- control Internet-related and Internet-communicated crime.
- monitor the billions of people on the Internet with varying opinions and preferences.
Thus, internet censorship acts as a viable method by governments and official organizations to manage what their citizens can view.
Who monitor internet consership
What are filters?
An internet content filter is a piece of software that, once installed on a computer, acts as a censor while you surf the web. Websites that are deemed offensive according to the criteria incorporated into the software program will be blocked so that you will not be able to view them with your web browser. Filters are currently installed on computers in public and school libraries, in workplaces and in many other settings. Some parents opt to install this software on their home computers in order to have better control of their children's internet use.
Filtering has been a hot topic in the public library community since web access first became a service provided to patrons. Those in favour of filters claim that they are an effective security measure that keeps out unwanted content and does not impact on users in any detrimental way. Those opposed to filters cite instances when legitimate research material has been blocked by filters and argue that it is an excessive measure that harms more than it helps. Others take the middle ground and contend that although filters are problematic, they are the only realistic method of ensuring that public libraries remain as safe environments.
https://cippic.ca/en/internet-censorship-in-public-libraries
A common complaint about filters is that they are not 100% effective in blocking out inappropriate material. Generally, Canadian public libraries warn patrons that filters are not perfect and that parents should monitor their children's internet use, even on filtered terminals.
However, there are laws that REQUIRE some libraries to place filters on internet use. The Children's Internet Protection Act (CIPA) of 2000 requires libraries that receive funding from LSTA sources, or benefit from a discount program called "E-rate," to filter their internet connections. The ALA describes its requirements as follows:
The law defines a “technology protection measure” as “a specific technology that blocks or filters Internet access to visual depictions that are— (A) obscene . . .; (B) child pornography . . .; or (C) harmful to minors . . .” Although the law clearly requires the use of filtering or blocking technology, it does not require the use of specific filtering software or services. Instead, CIPA requires schools or libraries covered by the new requirements to certify that they are using technology that blocks or filters access to visual depictions of the type specified in the legislation. (See ALA CIPA FAQ, http://www.ala.org/advocacy/site... )
Fear of Filtering - YouTube
censorship in public library
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nfGf1xhTMyQ
Debate About censership
The debate has recently boiled over in the U.S. with the enactment of the federal Children's Internet Protection Act. This legislation, in part, places a requirement on public libraries to implement content filters on their internet access terminals in exchange for certain federal funding. In response, the American Library Association initiated a legal battle to have this requirement struck down. In the summer of 2003, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the filtering for funding requirement was constitutional and would stand. The ruling has left the American library community deeply divided. On one side are library boards that have voted in favour of installing filters on all library terminals. On the other side are boards against any filtering. In the middle are boards that have decided to compromise and have filters installed on some, but not all, library terminals (usually on terminals in areas reserved for children).
Top 10 Countries With Highest Internet Censorship
**North Korea. All websites are under government control. ... **Burma. Authorities filter e-mails and block access to sites of groups that expose human rights violations or disagree with the government.**Cuba. Internet available only at government controlled "access points." ... **Saudi Arabia. ... **Iran. ... **China. ... **Syria. ... **Tunisia.
Top 10 Internet-censored countries - USA Today
www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2014/02/05/top-ten-internet-censors/5222385
| China | 88 |
| Syria | 87 |
| Iran | 87 |
| Ethopia | 83 |
| Uzbekistan | 79 |
| Cuba | 79 |
| Vietnam | 76 |
| Saudi Arabia | 72 |
| Bahrain | 71 |
| Pakistan69 Copuntries with freedom of consership Freedom on the Net 2016 (FOTN) report by Freedom House describes the state of internet freedom in different parts of the world. It says, as high as 67% of the internet populations around the world uses the internet that’s censored in some form. 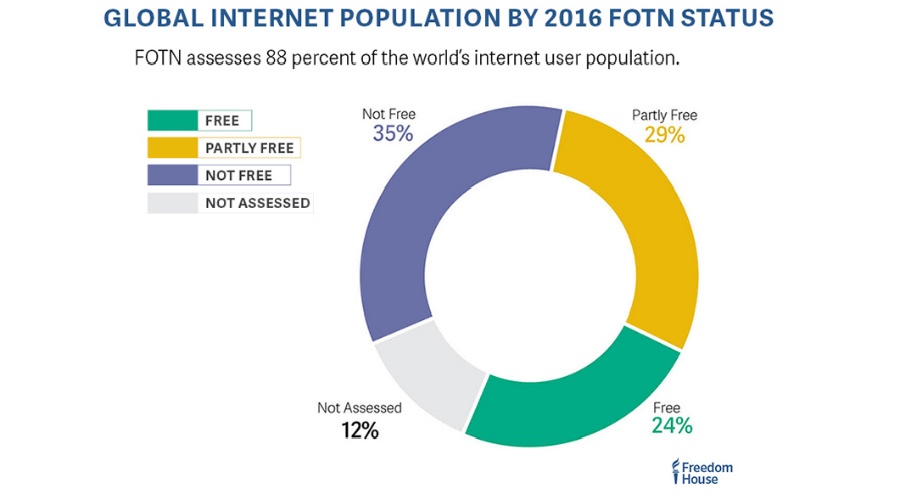 On looking at the world map generated using the data, it appears that the internet population in Asia is using a lot less ‘free’ internet than the population living in western continents like North and South America. And even in Europe, the internet is freer to a great extent. For Africa, where most of the land is not taken into consideration, the non-free internet exists. 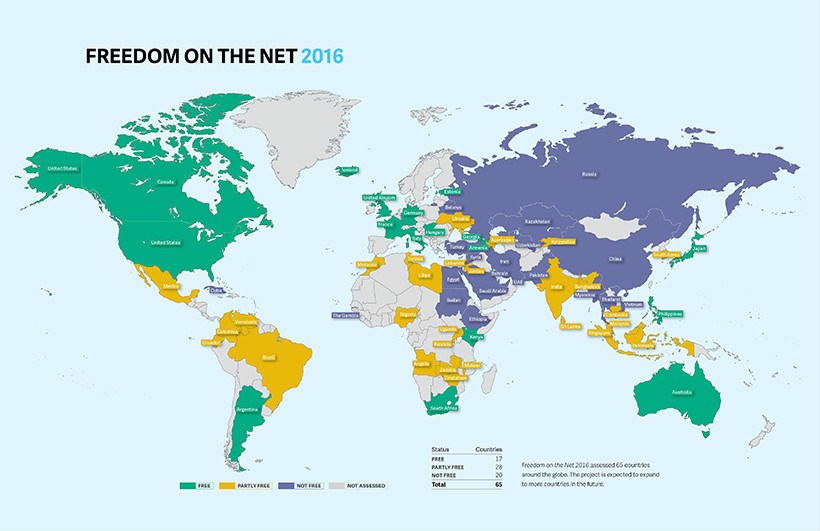 Asia accounts for a big chunk of internet population existing in China, India, Turkey, Pakistan, Japan, South Korea, Russia, etc. Countries with high censorship like China, Ethiopia, Iran, Syria, etc are ones to have a high FOTN score above 80, practically approaching towards the worst form of censorship. On the other hand, countries like Estonia, Iceland, Canada, US, Germany are top countries with lowest FOTN scores .https://fossbytes.com/countries-highest-internet-censorship/ Debate About censorship The debate has recently boiled over in the U.S. with the enactment of the federal Children's Internet Protection Act. This legislation, in part, places a requirement on public libraries to implement content filters on their internet access terminals in exchange for certain federal funding. In response, the American Library Association initiated a legal battle to have this requirement struck down. In the summer of 2003, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the filtering for funding requirement was constitutional and would stand. The ruling has left the American library community deeply divided. On one side are library boards that have voted in favour of installing filters on all library terminals. On the other side are boards against any filtering. In the middle are boards that have decided to compromise and have filters installed on some, but not all, library terminals (usually on terminals in areas reserved for children). https://youtu.be/zGgUmFKefNA |
Wednesday 3 May 2017
Libguide for Public Library
What is a
LibGuide?
•LibGuides is a web 2.0 content management and
publishing system created by SpringShare.
•LibGuides
is a hosted system which is run on the SpringShare servers. The company
provides support and upgrades. A library just needs to subscribe to the
service.
•Libraries
use it to: ◦integrate multimedia content into library services
◦promote
library resources to their users
◦create
subject guides, course guides, information portals, research help pages, etc.
Why libguides
LibGuides is an easy-to-use content management
system deployed at thousands of libraries worldwide. Librarians use it to curate
knowledge and share information, organize class and subject specific resources,
and to create and manage websites. Increase the usage of your library's
resources and content by showcasing them in LibGuides.
LibGuides
is one of the most flexible platforms I use. Not only can it do almost
anything, the interface is so intuitive that anyone can skillfully use it. I've
taught many folks at my school how to use LibGuides for their course-pages,
project descriptions, photo galleries, and more! Plus working with the folks at
Springshare is always a pleasure! -Trevor Calvert, Library Director-Marin
Academy
Can your patrons discover the wealth of electronic
and print resources your library offers?, LibGuides is an easy-to-use
no-technical-skills necessary web content management system designed for
librarians., You'll easily create and maintain gateways to point your patrons
to the resources they need - whether it's finding a great read, finding a job,
or finding their long-lost ancestors., And our full statistics tools will tell
you exactly what resources are being used, and where to focus your attention
next! Already in use in the state of Ohio by the following public libraries
LibGuides is an easy-to-use and affordable solution to your website woes: ___ _
Marysville Public Library - http://marysvillelib.org ___ _ Pickerington
Public Library - http://pickeringtonlibrary.org ___ _ State
Library of Ohio - http://library.ohio.libguides.com ___ _
Westerville Library - http://explore.westervillelibrary.org ,
Using
LibGuides to Enhance Library Services
By Embry,
Allison
Article excerpt
Using LibGuides to Enhance Library Services. Edited
by Aaron W. Dobbs, Ryan L. Sittler, and Douglas Cook. Chicago: ALA, 2013. 307
p. Paper $65 (ISBN 978-1-55570-880-1).
LibGuides
has become an indispensable tool to librarians and other information professionals.
Since Springshare first introduced the product in 2007, LibGuides has aided
more than five million library users worldwide, and its popularity continues to
grow. Dobbs, Sittler, and Cook's volume is a timely, well-organized collection
of articles addressing the most important question: How can librarians can best
implement and use LibGuides to serve their patron communities?
The book
is organized into five sections that cover the history of library guides,
administration of LibGuides, basic use of the LibGuides product, guide design,
and examples of exceptional guides. Both library staff and administrators will
find this book to be very informative; all articles in this volume are authored
by librarians who have used LibGuides, and real-world examples are cited to
show how this tool has been used to enhance library services. … https://www.questia.com/library/journal/1G1-351948550/using-libguides-to-enhance-library-services
The benefit of the Libguides
Reading book club
In its
broadest sense a "reading group" is a collection of people who come
together to discuss a variety of topics contained in books. It provides an
enjoyable social experience and creates a reader-focused environment in which
readers can explore the creativity of reading.
Benefits include
the following:
- reading groups build on libraries’ traditional core skills in promoting reading, informal learning and self-help.
- reading groups deliver benefits to society and to the individual. They provide support, for instance, for adult literacy and children’s learning
- reading group provision builds on libraries’ open, neutral and self-help culture and provides a distinctive service that, at the same time, shares common ground with private- and public-sector partners.
Public and community libraries are central players in the
reading group movement
In its
broadest sense a "reading group" is a collection of people who come
together to discuss a variety of topics contained in books. It provides an
enjoyable social experience and creates a reader-focused environment in which
readers can explore the creativity of reading.
Benefits include
the following:
- reading groups build on libraries’ traditional core skills in promoting reading, informal learning and self-help.
- reading groups deliver benefits to society and to the individual. They provide support, for instance, for adult literacy and children’s learning
- reading group provision builds on libraries’ open, neutral and self-help culture and provides a distinctive service that, at the same time, shares common ground with private- and public-sector partners.
Public and community libraries are central players in the
reading group movement
http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/c.php?g=492401&p=3387214t
http://libguides.unisa.ac.za/c.php?g=492401&p=3387214t
The power of using Libguides
Jill Rafter
& Paul Norko Clarksburg-Harrison Public Library
LibGuides CMS gave us a way to
involve more of our staff in adding and updating content on the website. We
wanted a way to share the burden of updating the site among the staff, instead
of on one person.
Before LibGuides CMS we had
just one person with primary responsibility for our site. LibGuides CMS helped
us share that responsibility among a number of staff members. It was relatively
easy to learn and staff are free to add updates and new content when they need
it instead of waiting for someone else to add it.
The sandbox-style
form building in LibWizard have helped the most, since I’m not the greatest
with HTML and other coding used to build these things (though I understand the
basics of it). It would take a lot longer to build and get working correctly if
I had to write the code myself. http://clarksburglibrary.info/home
- Paul Norko
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)